Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
TransPixar: Advancing Text-to-Video Generation with Transparency
TransPixar: Advancing Text-to-Video Generation with Transparency
Luozhou Wang Yijun Li Zhifei Chen Jui-Hsien Wang Zhifei Zhang He Zhang Zhe Lin Yingcong Chen
Abstract
Text-to-video generative models have made significant strides, enabling diverse applications in entertainment, advertising, and education. However, generating RGBA video, which includes alpha channels for transparency, remains a challenge due to limited datasets and the difficulty of adapting existing models. Alpha channels are crucial for visual effects (VFX), allowing transparent elements like smoke and reflections to blend seamlessly into scenes. We introduce TransPixeler, a method to extend pretrained video models for RGBA generation while retaining the original RGB capabilities. TransPixar leverages a diffusion transformer (DiT) architecture, incorporating alpha-specific tokens and using LoRA-based fine-tuning to jointly generate RGB and alpha channels with high consistency. By optimizing attention mechanisms, TransPixar preserves the strengths of the original RGB model and achieves strong alignment between RGB and alpha channels despite limited training data. Our approach effectively generates diverse and consistent RGBA videos, advancing the possibilities for VFX and interactive content creation.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from HKUST(GZ), HKUST, and Adobe Research propose TransPixeler, a LoRA-enhanced DiT-based method with an alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism that enables high-fidelity RGBA video generation from text while preserving RGB quality, advancing visual effects and interactive content creation through joint RGB-alpha modeling despite limited training data.
Key Contributions
- TransPixeler addresses the challenge of RGBA video generation—critical for visual effects and interactive content—by extending pretrained DiT-based text-to-video models to jointly generate RGB and alpha channels, overcoming the limitations of scarce RGBA training data and unidirectional generation pipelines.
- The method introduces alpha-specific tokens and a modified attention mechanism that preserves RGB generation quality while enabling bidirectional alignment between RGB and alpha channels, with LoRA-based fine-tuning applied only to alpha-related projections to minimize interference.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate TransPixeler’s ability to generate diverse, high-fidelity RGBA videos with strong RGB-alpha consistency, outperforming generation-then-prediction approaches on challenging compositions like smoke, reflections, and transparent objects.
Introduction
The authors leverage diffusion transformer (DiT)-based text-to-video models to enable RGBA video generation—producing videos with transparent alpha channels—while preserving the high-quality RGB generation capabilities of pretrained models. This is critical for visual effects in gaming, VR, AR, and film, where transparent elements like smoke, glass, or reflections must seamlessly integrate into scenes. Prior approaches either relied on post-hoc video matting, which struggles with generalization and temporal consistency, or used separate RGB-first and alpha-prediction pipelines that suffer from poor alignment and limited data. These methods are further constrained by the scarcity of RGBA video datasets, with only around 484 videos available. The authors’ main contribution is TransPixeler, a method that extends DiT models with alpha-specific tokens and a novel alpha channel adaptive attention mechanism. By using LoRA-based fine-tuning focused only on alpha-related projections and carefully designing attention interactions—such as enabling RGB-to-alpha attention while removing text-to-alpha attention—they achieve strong RGB-alpha alignment with minimal parameter updates. This allows high-fidelity, diverse RGBA video generation from text, even with limited training data, effectively bridging the gap between RGB-only models and the demands of advanced visual effects.
Method
The authors leverage a diffusion transformer (DiT) architecture to extend existing RGB video generation models for joint text-to-RGBA video synthesis. The core framework builds upon a pre-trained DiT model, which processes a combined sequence of text and video tokens using full self-attention. The input sequence consists of text tokens xtext and video tokens xvideo, both of shape B×L×D, where B is the batch size, L is the sequence length, and D is the latent dimension. These tokens are concatenated into a single sequence, and the standard self-attention mechanism is applied across the combined sequence. The attention computation is defined as Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(dkQKT)V, where the query, key, and value representations are derived from the input tokens via projection matrices Wt and a positional encoding function ft.
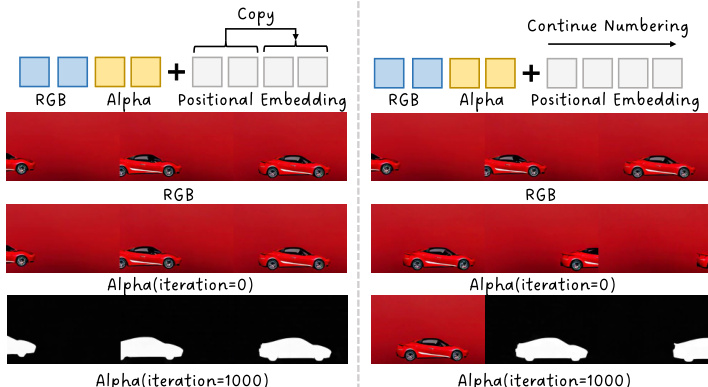
The proposed method, TransPixeler, introduces several key modifications to the base DiT architecture to enable the generation of alpha channels. First, the input sequence length is doubled to accommodate both RGB and alpha video tokens. The original L video tokens are used to generate the RGB video, while a new set of L alpha tokens is appended to generate the alpha video. This sequence extension is illustrated in the framework diagram. To ensure the model can effectively learn the distinct characteristics of the two domains, the positional encoding function is modified. Instead of assigning unique positional indices to RGB and alpha tokens, the method shares the same positional encoding for both domains. This is achieved by reinitializing the positional embedding for alpha tokens using the same positional indices as the corresponding RGB tokens, with an additional learnable domain embedding d to differentiate the two modalities. This design choice helps to minimize spatial-temporal alignment challenges during the initial training phase, accelerating convergence.
To further improve the model's ability to generate high-quality alpha videos, the authors employ a fine-tuning scheme using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). The LoRA layer is applied selectively to the alpha domain tokens, allowing the model to adapt its parameters specifically for alpha generation without disrupting the pre-trained behavior for RGB generation. This selective adaptation is implemented by modifying the weight matrices for the alpha tokens, where the updated weights are a combination of the original weights and a low-rank update term controlled by a residual strength γ. The attention mechanism is also rectified through the use of a custom attention mask. This mask blocks the computation of attention from text tokens to alpha tokens, which is detrimental to generation quality due to the domain gap between text and alpha. The mask is defined as Mmn∗=−∞ if m≤Ltext and n>Ltext+L, and 0 otherwise. This ensures that text tokens do not attend to alpha tokens, preserving the model's original behavior in the text and RGB domains.
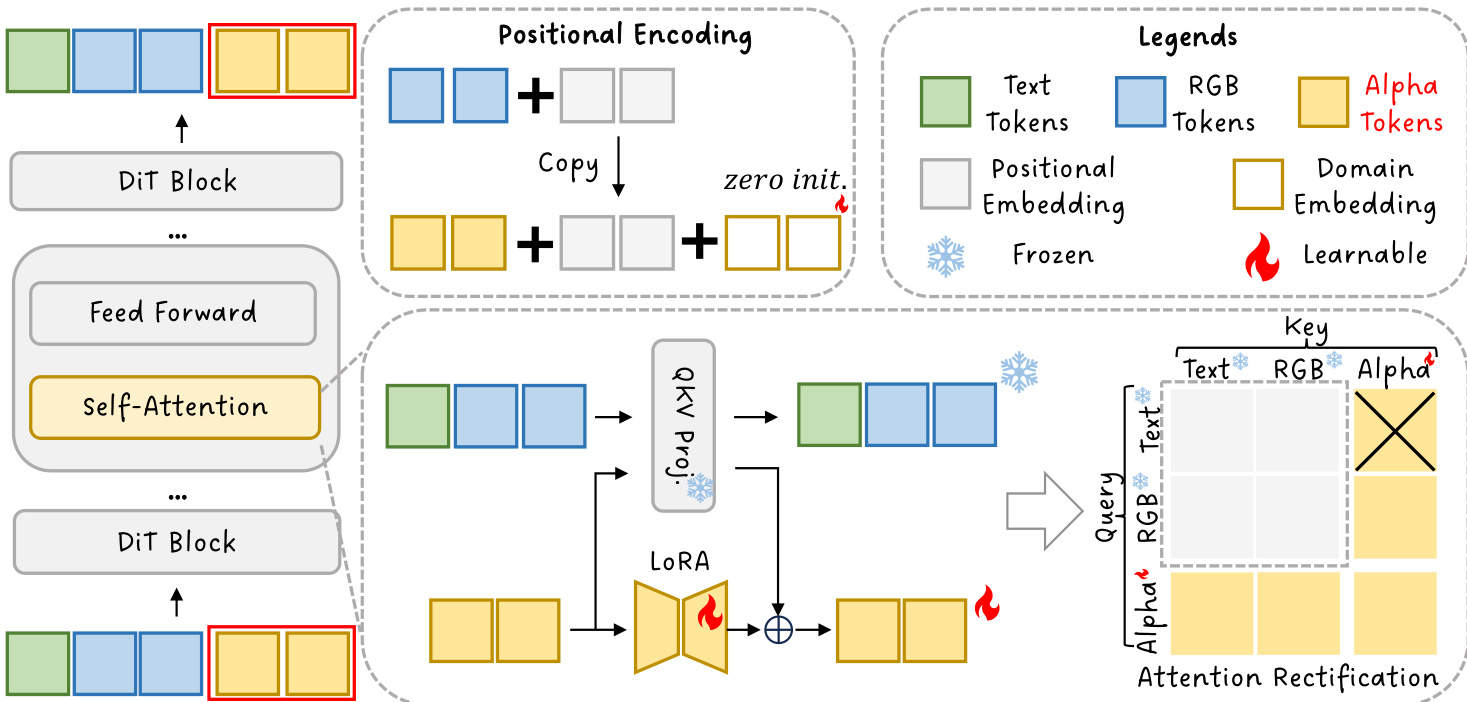
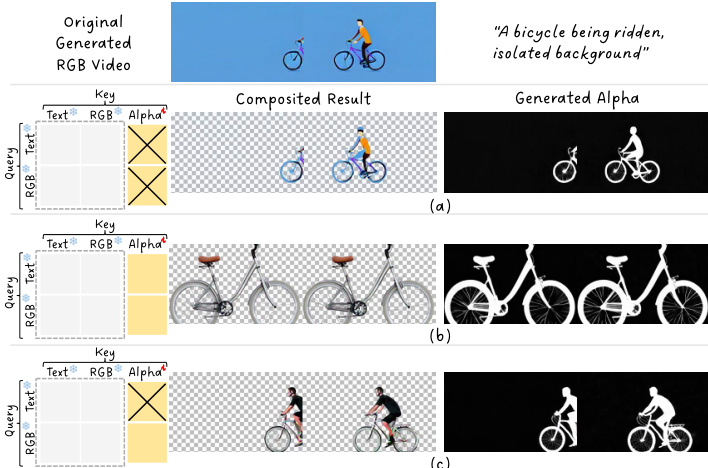
The overall inference process combines these modifications. The query, key, and value representations are computed from the concatenated text and video tokens, with the modified positional encoding function applied to the video tokens. The attention mechanism then uses the rectified attention mask to compute the final attention output. The authors analyze the attention matrix, which is organized into a 3x3 grouped structure, to understand the interactions between different token types. They find that while text-to-alpha attention is harmful and must be blocked, RGB-to-alpha attention is essential for refining the RGB generation by providing alpha guidance. This analysis leads to the design of the attention rectification strategy, which balances the preservation of RGB quality with the accurate generation of alpha channels.
Experiment
- Text-to-Video with Transparency: Demonstrates generation of dynamic objects with motion (spinning, running, flying) and transparent materials (bottles, glasses), along with complex effects like fire, explosions, cracking, and lightning, validating robustness in handling transparency and motion.
- Image-to-Video with Transparency: Integrates with CogVideoX-I2V to generate videos from a single image with optional alpha channel, automatically propagating or generating alpha channels for subsequent frames, showing effective transparency and motion consistency.
- Comparison with Generation-then-Prediction: Outperforms Lotus + RGBA and SAM-2 in qualitative alignment of RGB and alpha channels, especially for non-human objects and complex visual effects, as shown in Fig. 7.
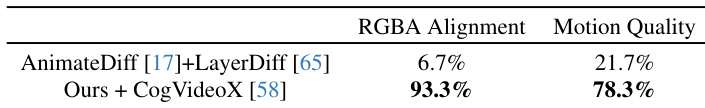
- Comparison with Joint Generation: Surpasses LayerDiffusion + AnimateDiff in motion fidelity and RGB-alpha alignment, as illustrated in Fig. 8, with user study (87 participants, 30 videos) showing significant preference for our method in both alignment and prompt adherence.
- Ablation Study: Validates the importance of RGB-to-Alpha attention for alignment; removing it degrades motion quality and causes misalignment. Alternative designs (Batch and Latent Dimension extensions) show inferior performance; our DiT sequence extension achieves optimal balance.
- Quantitative Evaluation: Achieves low flow difference (high motion alignment) and low FVD (high generative quality), demonstrating effective trade-off between alignment and motion fidelity on 80 generated 64-frame videos.
- Limitations: Quadratic computational cost due to sequence expansion; performance depends on the underlying T2V model’s generative priors; future work will explore efficiency optimizations.
Results show that the proposed method combined with CogVideoX achieves significantly higher RGBA alignment at 93.3% and motion quality at 78.3% compared to the baseline method AnimateDiff + LayerDiff, which scores 6.7% and 21.7% respectively. This indicates that the proposed approach better aligns the alpha channel with RGB content while preserving motion quality.