Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
HunyuanCustom: A Multimodal-Driven Architecture for Customized Video
Generation
HunyuanCustom: A Multimodal-Driven Architecture for Customized Video Generation
Teng Hu Zhentao Yu Zhengguang Zhou Sen Liang Yuan Zhou Qin Lin Qinglin Lu
Abstract
Customized video generation aims to produce videos featuring specific subjects under flexible user-defined conditions, yet existing methods often struggle with identity consistency and limited input modalities. In this paper, we propose HunyuanCustom, a multi-modal customized video generation framework that emphasizes subject consistency while supporting image, audio, video, and text conditions. Built upon HunyuanVideo, our model first addresses the image-text conditioned generation task by introducing a text-image fusion module based on LLaVA for enhanced multi-modal understanding, along with an image ID enhancement module that leverages temporal concatenation to reinforce identity features across frames. To enable audio- and video-conditioned generation, we further propose modality-specific condition injection mechanisms: an AudioNet module that achieves hierarchical alignment via spatial cross-attention, and a video-driven injection module that integrates latent-compressed conditional video through a patchify-based feature-alignment network. Extensive experiments on single- and multi-subject scenarios demonstrate that HunyuanCustom significantly outperforms state-of-the-art open- and closed-source methods in terms of ID consistency, realism, and text-video alignment. Moreover, we validate its robustness across downstream tasks, including audio and video-driven customized video generation. Our results highlight the effectiveness of multi-modal conditioning and identity-preserving strategies in advancing controllable video generation. All the code and models are available at https://hunyuancustom.github.io.
One-sentence Summary
The authors propose HunyuanCustom, a multi-modal video generation framework developed by Tencent's Hunyuan team and collaborators, which achieves superior subject identity consistency across text, image, audio, and video inputs through a text-image fusion module, image ID enhancement via temporal concatenation, and modality-specific condition injection mechanisms—enabling advanced applications in virtual humans, singing avatars, and video editing with enhanced controllability and realism.
Key Contributions
-
HunyuanCustom addresses the challenge of subject-consistent video generation under diverse user-defined conditions, overcoming limitations in identity preservation and modality flexibility found in existing methods that typically support only image or text inputs.
-
The framework introduces a text-image fusion module based on LLaVA and an image ID enhancement module using temporal concatenation to strengthen identity features across frames, while also proposing modality-specific condition injection mechanisms—AudioNet for hierarchical audio-video alignment and a patchify-based video-latent alignment module for video-driven generation.
-
Extensive evaluations on single- and multi-subject scenarios demonstrate HunyuanCustom's superiority over state-of-the-art open- and closed-source models in identity consistency, realism, and text-video alignment, with validated robustness across audio- and video-driven customization tasks.
Introduction
The authors leverage recent advances in diffusion-based video generation to address the persistent challenge of subject-consistent, fine-grained video customization. While prior methods excel in text- or image-driven generation, they often fail to maintain identity fidelity across multiple subjects or modalities, particularly when extending to audio or video inputs. Many existing approaches rely on instance-specific fine-tuning or single-modality conditioning, limiting scalability and real-time applicability. The authors introduce HunyuanCustom, a multi-modal video generation framework that enables robust, subject-consistent video synthesis conditioned on text, images, audio, and video. It achieves this through a novel text-image fusion module based on LLaVA, an image ID enhancement module using temporal concatenation, and dedicated condition injection mechanisms for audio and video. For audio-driven generation, AudioNet enables hierarchical audio-video alignment via spatial cross-attention, while a video patchify and identity-disentangled conditioning module ensures effective video-latent feature integration. Evaluated across single- and multi-subject scenarios, HunyuanCustom outperforms existing open-source and commercial models in identity consistency, video quality, and multi-modal alignment, demonstrating strong potential for applications in virtual avatars, advertising, and interactive video editing.
Dataset
-
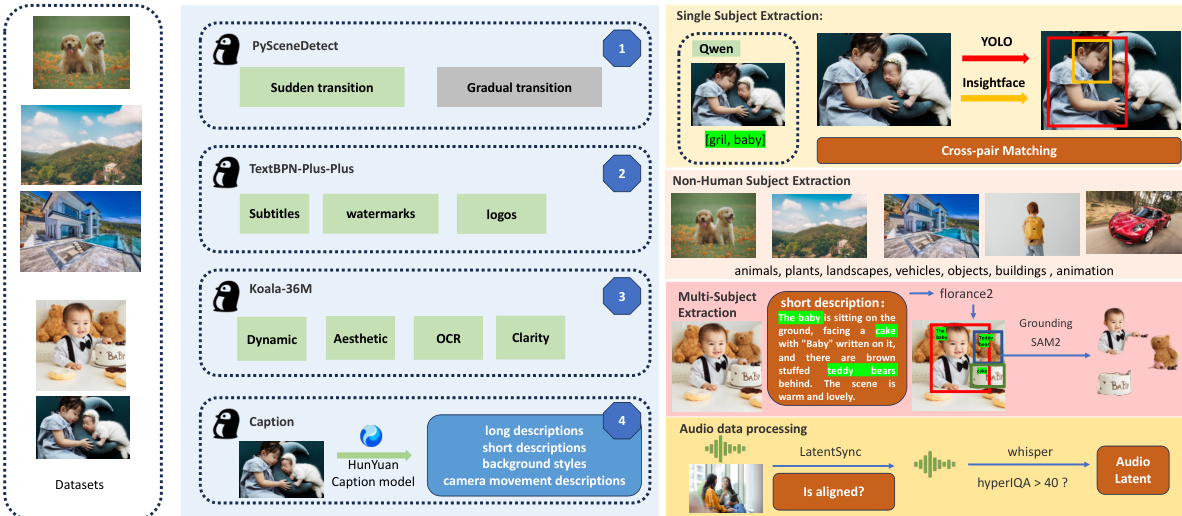
The dataset is composed of video data sourced from diverse channels, including self-collected content and curated open-source datasets such as OpenHumanvid. It covers eight primary domains: humans, animals, plants, landscapes, vehicles, objects, architecture, and anime, ensuring broad domain coverage and diversity.
-
Data preprocessing includes segmentation into single-shot clips using PySceneDetect to avoid intra-video transitions. Clips with excessive text, subtitles, watermarks, or logos are filtered out using textbn-plus-plus. Videos are cropped and resized to standardize the short side to either 512 or 720 pixels, with a maximum length of 5 seconds (129 frames). A final refinement step uses the koala-36M model with a custom threshold of 0.06 to filter for aesthetic quality, motion magnitude, and scene brightness, addressing limitations in existing tools.
-
Subject extraction is performed differently based on subject type:
- For humans, Qwen7B labels subjects per frame, and a Union-Find clustering algorithm identifies the most frequent subject ID (minimum 50 frames). YOLO11X and InsightFace are used for body and face detection, with face bounding boxes discarded if they occupy less than 50% of the body box.
- For non-humans, QwenVL extracts keywords, and GroundingSAM2 generates masks and bounding boxes; boxes smaller than 0.3× the video dimensions are discarded. Subjects are classified into one of eight categories, and balanced sampling ensures even distribution.
- For multi-subject videos, Florence2 extracts bounding boxes from video captions, followed by GroundingSAM2 for mask generation. Clustering removes frames missing any subject, and the first 5 seconds are used for training while the next 15 seconds are reserved for segmentation.
-
Video resolution standardization involves computing a union bounding box of all main subjects and ensuring the cropped region retains at least 70% of that area. The dataset supports multiple aspect ratios—1:1, 3:4, and 9:16—to enable multi-resolution output.
-
Video annotations are generated using a HunYuan-developed structured annotation model, providing detailed metadata including long and short descriptions, background styles, and camera movement details. These annotations enrich video captions and improve model robustness.
-
Mask data augmentation is applied during training to prevent overfitting. Techniques such as mask dilation and conversion to bounding boxes soften mask boundaries, improving generalization when editing objects with varying shapes or features (e.g., replacing a doll with or without ears).
-
Audio data is processed using LatentSync to assess audio-video synchronization, discarding clips with confidence below 3 and aligning audio to video at zero offset. HyperIQA scores below 40 are removed to ensure high audio quality. Whisper is used to extract audio features for model training.
Method
The authors leverage the HunyuanVideo framework as the foundation for HunyuanCustom, a multi-modal customized video generation model designed to maintain subject identity across diverse input conditions. The overall architecture is structured to support four primary tasks: text-driven, image-driven, audio-driven, and video-driven video generation, all centered on subject consistency. As shown in the figure below, the framework integrates distinct modules for each modality, enabling decoupled control over image, audio, and video conditions while preserving identity information.
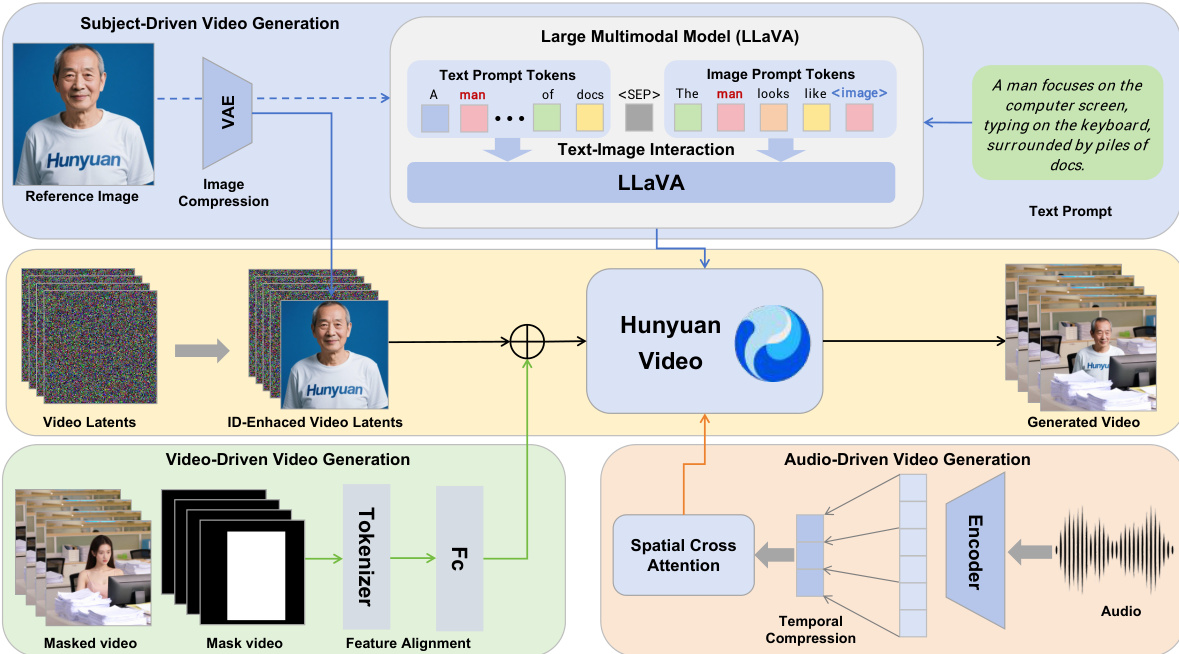
At the core of the image-driven customization is a text-image fusion module based on LLaVA, which facilitates interaction between visual and textual inputs. This module processes a text prompt and an input image by constructing a template that either embeds the image token within the text or appends it after the text, with a special separator token to prevent the image features from dominating the text comprehension. The image token is replaced by 24×24 image hidden features extracted by LLaVA, enabling joint modeling of the visual and textual information. To enhance identity consistency throughout the generated video, an identity enhancement module is introduced. This module concatenates the image latent, obtained by mapping the reference image to the latent space using a pretrained causal 3DVAE, with the noisy video latent along the temporal dimension. The concatenated latent is then assigned a 3D-RoPE along the time series, with the image latent positioned at the -1-th frame to broadcast identity information. A spatial shift is applied to the image latents to prevent the model from simply copying the image into the generated frames.
For multi-subject customization, the model extends the single-subject approach by encoding multiple condition images into latent space and concatenating them with the video latent. Each image is assigned a unique time index and corresponding 3D-RoPE to differentiate between identities. The training process employs a Flow Matching framework, where the model predicts the velocity of the video latent conditioned on the target image. The loss function minimizes the mean-squared error between the predicted and real velocities, and both the video generation model and the LLaVA model are fully fine-tuned to unlock the model's full potential.
To support audio-driven video customization, the authors propose an Identity-disentangled AudioNet module. This module aligns audio features with the compressed video latent by padding and aggregating the audio frames. A spatial cross-attention mechanism is then used to inject audio information into the video latent on a per-frame basis, preventing inter-frame interference. The audio features are processed through a cross-attention module, and the resulting features are added to the video latent with a learnable weight to control the influence of the audio.
For video-driven video customization, HunyuanCustom adopts an efficient video condition injection strategy. The conditioning video is compressed using the pretrained causal 3D-VAE and aligned with the video latents via a feature alignment network. The conditioned features are then either concatenated or added to the video latents on a frame-by-frame basis, preserving the original feature dimensions and introducing no additional computational overhead during inference. The addition-based method is found to be more effective in preserving content information and enabling efficient fusion of the conditioning video features with the video latents.
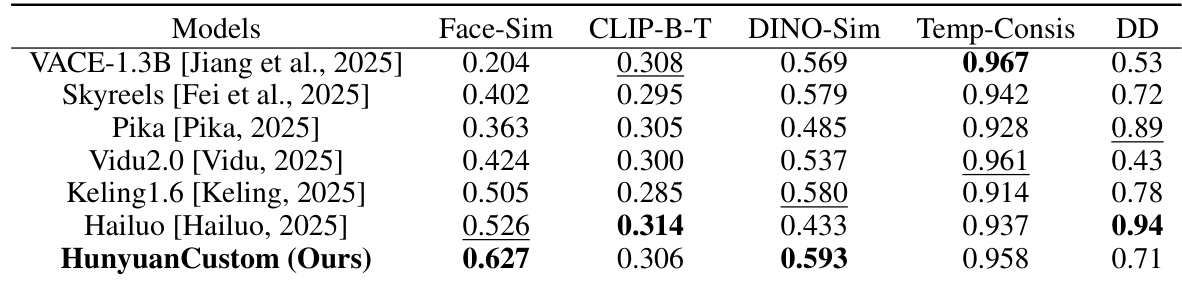
Experiment
- Conducted comprehensive experiments on single-subject and multi-subject video customization, evaluating identity preservation, text-video alignment, temporal consistency, and dynamic movement.
- On single-subject tasks, HunyuanCustom achieved the best ID consistency and subject similarity, outperforming state-of-the-art methods including Vidu 2.0, Keling 1.6, Pika, Hailuo, Skyreels-A2, and VACE, with superior video quality and prompt adherence.
- On multi-subject tasks, HunyuanCustom demonstrated strong capability in maintaining both human and non-human subject identities, with stable, high-quality generation and natural interactions, enabling novel applications such as virtual human advertising.
- In video-driven customization, HunyuanCustom excelled in video subject replacement, avoiding boundary artifacts and copy-paste effects seen in VACE and Keling, while ensuring seamless integration and identity preservation.
- Ablation studies confirmed the necessity of LLaVA for identity feature extraction, the effectiveness of the identity enhancement module in capturing fine-grained details, and the superiority of temporal concatenation over channel concatenation in maintaining generation quality and identity fidelity.
Results show that HunyuanCustom achieves the highest face similarity and subject similarity among all compared models, indicating strong identity preservation. It also demonstrates competitive performance in text-video alignment and temporal consistency, while maintaining a high dynamic degree, outperforming most baselines in overall video quality and consistency.