Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Fast Conformer with Linearly Scalable Attention for Efficient Speech Recognition
Fast Conformer with Linearly Scalable Attention for Efficient Speech Recognition
Abstract
Conformer-based models have become the dominant end-to-end architecture for speech processing tasks. With the objective of enhancing the conformer architecture for efficient training and inference, we carefully redesigned Conformer with a novel downsampling schema. The proposed model, named Fast Conformer(FC), is 2.8x faster than the original Conformer, supports scaling to Billion parameters without any changes to the core architecture and also achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on Automatic Speech Recognition benchmarks. To enable transcription of long-form speech up to 11 hours, we replaced global attention with limited context attention post-training, while also improving accuracy through fine-tuning with the addition of a global token. Fast Conformer, when combined with a Transformer decoder also outperforms the original Conformer in accuracy and in speed for Speech Translation and Spoken Language Understanding.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from NVIDIA and UCLA propose Fast Conformer, a redesigned Conformer architecture with a novel downsampling scheme that achieves 2.8× faster training and inference, scales to billion parameters, and delivers state-of-the-art accuracy in speech recognition, translation, and spoken language understanding, leveraging limited context attention and a global token for long-form speech up to 11 hours.
Key Contributions
- The paper addresses the high computational cost and limited scalability of Conformer models by redesigning the downsampling schema to achieve 8x downsampling through three depth-wise convolutional layers, reducing sequence length and cutting global attention compute by 2.9x, enabling 2.8× faster inference without altering the core architecture.
- To support long-form speech up to 11 hours, the authors replace global attention with limited context attention post-training and introduce a global token for fine-tuning, improving accuracy while maintaining linear scalability with sequence length.
- Fast Conformer achieves state-of-the-art results on Automatic Speech Recognition benchmarks and outperforms the original Conformer in both speed and accuracy for Speech Translation and Spoken Language Understanding, with open-sourced models and training recipes available via NVIDIA NeMo.
Introduction
The authors address the challenge of efficient speech recognition in large-scale applications, where conventional Conformer models face high computational costs due to quadratic complexity in self-attention mechanisms. This limits their deployment in real-time or resource-constrained environments despite strong accuracy. To overcome this, they introduce a FAST Conformer architecture that replaces standard attention with a linearly scalable attention mechanism, significantly reducing both memory usage and inference time while preserving recognition accuracy. The key contribution is a novel attention design that maintains model performance across diverse speech datasets while enabling scalable deployment on hardware with limited resources.
Dataset
- The dataset comprises audio and text data from three primary sources: Multilingual LibriSpeech (MLS), Mozilla Common Voice (MCV), and Wall Street Journal (WSJ).
- The authors first trained baseline and Fast Conformer models exclusively on LibriSpeech, using a SentencePiece unigram tokenizer with 128 tokens for CTC models and 1024 tokens for RNNT models.
- Training employed the AdamW optimizer with a Noam learning rate scheduler for baseline models, using peak learning rates of 0.0025 (RNNT) and 0.001 (CTC), and a linear warmup over 15,000 steps. Fast Conformer models used a cosine learning rate scheduler with peak rates of 0.005 (RNNT) and 0.001 (CTC).
- Baseline Conformer-RNNT and -CTC models were trained for 80,000 steps, while CTC models ran for 380,000 steps. All models were trained on 32 GPUs with a global batch size of 2048.
- The final model weights were obtained by averaging the last five checkpoints to improve stability and performance.
- Model efficiency was evaluated using the DeepSpeed profiler to estimate Multiply Accumulate operations (MACs) for a single 30-second audio segment, with results summarized in Table 4.
- Fast Conformer models achieved slightly higher accuracy than standard Conformer models and demonstrated a 3x improvement in compute efficiency, while also outperforming EfficientConformer and SqueezeFormer in speed.
- Table 3 reports the maximum audio duration (in minutes) that can be transcribed in a single batch on an A100 GPU, providing insight into real-time inference capabilities.
Method
The authors leverage a redesigned Conformer architecture, termed Fast Conformer (FC), to achieve significant improvements in inference speed and scalability while maintaining competitive accuracy on speech processing tasks. The core of the redesign centers on a novel downsampling schema that increases the overall downsampling rate from 4x to 8x, thereby reducing the sequence length of the encoder output. This is achieved through a series of modifications to the initial sub-sampling block. The original Conformer employs a 4x downsampling module, which increases the frame rate from 10 ms to 40 ms. In contrast, Fast Conformer introduces three depth-wise convolutional sub-sampling layers to achieve an 8x downsampling, increasing the frame rate to 80 ms. This change reduces the computational and memory burden of the subsequent attention layers by a factor of 4, as they operate on a sequence that is 4x shorter. The sub-sampling block is further optimized by replacing the standard convolutional layers with depthwise separable convolutions, reducing the number of channels from 512 to 256, and decreasing the kernel size from 31 to 9. These modifications collectively contribute to a 2.8x speedup in encoder inference compared to the original Conformer. The overall framework of the downsampling process is illustrated in the figure below, which compares the sampling rates across different models.
To address the scalability limitations of standard self-attention in long-form audio transcription, the authors implement a limited context attention mechanism inspired by LongFormer. This approach replaces the global attention layers with a combination of local attention and a single global context token. In this design, each token attends only to a fixed-size window of neighboring tokens, significantly reducing the computational complexity from quadratic to linear with respect to sequence length. A single global token is introduced to capture long-range dependencies by attending to all other tokens and being attended to by all other tokens, using separate linear projections. This hybrid attention mechanism enables the model to process much longer audio sequences, extending the maximum duration from 15 minutes to 675 minutes on a single A100 GPU. The attention patterns for full context, limited context, and limited context with a global token are shown in the figure below.
Experiment
- Fast Conformer was evaluated on LibriSpeech and large-scale 25k-hour English ASR datasets, achieving competitive WER results with 2.9x less compute than Conformer; on LibriSpeech test-other, it surpassed Conformer in most benchmarks.
- On the 25k-hour ASR set, Fast Conformer-Large outperformed Conformer across multiple test sets including MLS, MCV, and WSJ-93, with RNNT and CTC decoders showing strong performance.
- In speech translation (English to German), Fast Conformer-RNNT achieved a BLEU score of 27.89 on MUST-C V2, with up to 1.84× faster inference than Conformer, despite RNNT's monotonic alignment limitation.
- For spoken language understanding (SLURP dataset), Fast Conformer-based models achieved intent accuracy and SLURP-F1 close to Conformer, with 10% faster inference, outperforming HuBERT-based baselines pre-trained on 60k hours of speech.
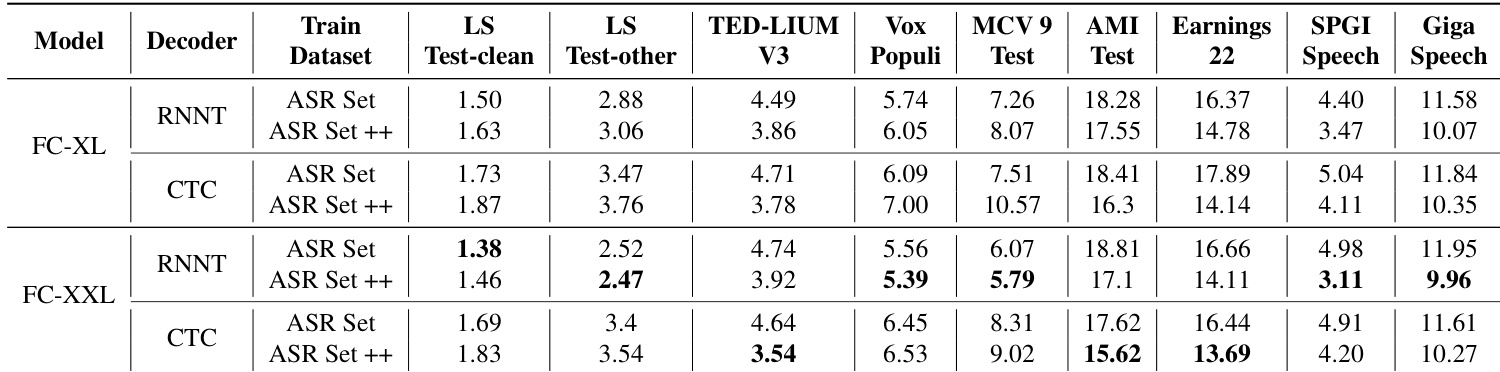
- Scaling experiments showed that Fast Conformer-XL and Fast Conformer-XXL models, trained on 25k hours and further augmented with 40k additional hours (ASR Set++), achieved state-of-the-art performance on HF-Leaderboard, with FC-XXL showing improved noise robustness across SNR levels.
- Fast Conformer-XXL trained on 65k hours (25k + 40k) achieved superior accuracy and robustness, demonstrating effective scaling of both model size and dataset size.
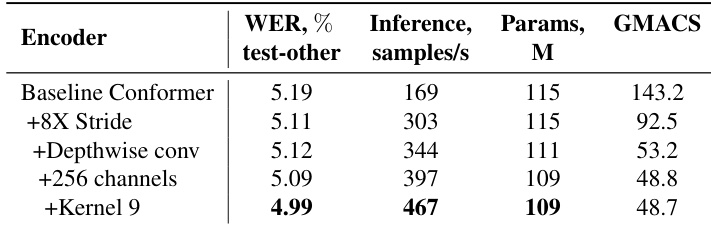
The authors compare different Conformer variants based on their subsampling schema and computational efficiency. Results show that Fast Conformer achieves a significant reduction in compute with a K value of 9, compared to 31 for Conformer and Squeezeformer, while using a depth-wise separable convolution scheme.

The authors use Fast Conformer to achieve a lower WER compared to Conformer on the LibriSpeech test-other set while using significantly less compute. Results show that Fast Conformer reduces encoder compute by 66% and parameters by 5% for RNNT and CTC decoders, maintaining competitive accuracy.
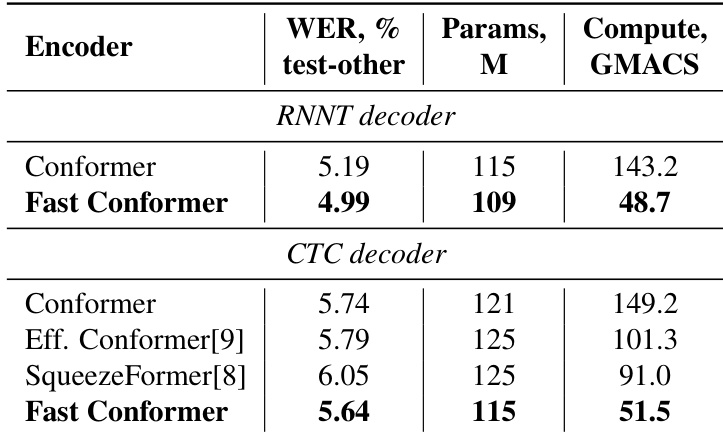
The authors compare Fast Conformer against ESPNet-SLU and SpeechBrain-SLU on the SLURP dataset for spoken language understanding. Results show that Fast Conformer achieves higher intent accuracy and SLURP-F1 scores while being 10% faster in inference compared to Conformer, despite using a smaller pre-trained encoder.
The authors evaluate Fast Conformer models FC-XL and FC-XXL on multiple ASR benchmarks, showing that FC-XXL achieves lower WER than FC-XL across most datasets, particularly on LS Test-other and MCV 9 Test. When trained on the augmented ASR Set++, FC-XXL further reduces WER on several benchmarks, demonstrating improved accuracy and noise robustness.
The authors evaluate the impact of architectural modifications on the Conformer encoder, showing that adding a kernel size of 9 reduces the WER on LibriSpeech test-other from 5.19% to 4.99% while increasing inference speed from 169 to 467 samples per second. These improvements are achieved with fewer parameters and lower compute requirements compared to the baseline Conformer.