Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
KV-Edit: Training-Free Image Editing for Precise Background Preservation
KV-Edit: Training-Free Image Editing for Precise Background Preservation
Tianrui Zhu Shiyi Zhang Jiawei Shao Yansong Tang
Abstract
Background consistency remains a significant challenge in image editing tasks. Despite extensive developments, existing works still face a trade-off between maintaining similarity to the original image and generating content that aligns with the target. Here, we propose KV-Edit, a training-free approach that uses KV cache in DiTs to maintain background consistency, where background tokens are preserved rather than regenerated, eliminating the need for complex mechanisms or expensive training, ultimately generating new content that seamlessly integrates with the background within user-provided regions. We further explore the memory consumption of the KV cache during editing and optimize the space complexity to O(1) using an inversion-free method. Our approach is compatible with any DiT-based generative model without additional training. Experiments demonstrate that KV-Edit significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of both background and image quality, even surpassing training-based methods. Project webpage is available at https://xilluill.github.io/projectpages/KV-Edit
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Tsinghua University and China Telecom propose KV-Edit, a training-free method for consistent image editing that preserves background key-value pairs in DiT-based models, enabling seamless content integration without complex mechanisms or retraining, achieving superior background fidelity and efficiency with O(1) memory complexity.
Key Contributions
- Background consistency in image editing is challenging due to the trade-off between preserving original content and aligning with new prompts, which existing training-free methods often fail to resolve without complex mechanisms or extensive tuning.
- KV-Edit introduces a training-free approach that leverages key-value cache in DiT architectures to preserve background tokens during inversion and denoising, ensuring perfect background consistency by reconstructing only the masked foreground region while seamlessly integrating new content.
- The method achieves state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets, outperforming both training-free and training-based approaches in background fidelity and image quality, while an inversion-free variant reduces memory complexity to O(1) for practical deployment.
Introduction
The authors leverage the key-value (KV) cache mechanism from transformer architectures to enable training-free image editing with precise background preservation. In text-to-image generation, especially with DiT-based flow models, maintaining background consistency during editing has been a persistent challenge, as prior training-free methods relying on attention modification or inversion samplers often fail to fully preserve original background content, while training-based approaches incur high computational costs. The key innovation of KV-Edit is to cache the KV pairs of background tokens during the inversion process and reuse them during denoising, ensuring the background remains unchanged while only the foreground is regenerated based on a new prompt. This approach achieves perfect background consistency without additional training, minimal hyperparameter tuning, and is compatible with any DiT-based model. The authors further optimize memory usage by integrating an inversion-free strategy, reducing space complexity to O(1), and introduce mask-guided inversion and reinitialization techniques to improve alignment with editing instructions, particularly in removal scenarios. Experiments show that KV-Edit outperforms both training-free and training-based methods in background fidelity and overall image quality.
Method
The authors leverage a diffusion-based framework to address the challenge of preserving background regions during image editing. The core methodology, termed KV-Edit, operates within a deterministic diffusion model framework, such as Rectified Flow, which models the transformation from noise to a real image as a continuous path governed by an ordinary differential equation (ODE). This ODE describes a reversible process where the model learns to predict velocity vectors that guide the denoising trajectory. The framework is built upon a DiT (Diffusion Transformer) architecture, which relies heavily on attention mechanisms, enabling a novel approach to decoupling foreground and background processing.
The overall framework begins with an inversion process, where the input image is progressively transformed into noise over a series of timesteps. During this process, the authors introduce a key innovation: an attention decoupling mechanism. This mechanism modifies the standard self-attention computation by using only foreground tokens as queries, while the keys and values are derived from the full image, including both foreground and background. This design allows the model to generate foreground content independently, ensuring that the background information remains isolated and unaltered during the generation phase. The process is illustrated in the framework diagram, where the input image is split into foreground and background components based on a provided mask.

Following the inversion, the method employs a KV cache to store the key-value pairs corresponding to the background regions at each timestep and layer of the model. This cache is then used during the denoising phase to reconstruct the background. The denoising process starts from a new foreground input, which is typically a noise vector or a modified version of the original foreground. The model then generates the final image by combining the regenerated foreground with the preserved background, using the cached key-value pairs to ensure consistency. This approach effectively circumvents the three main factors contributing to background inconsistency in traditional inversion-denoising paradigms: error accumulation, the influence of new conditions, and the impact of new foreground content.
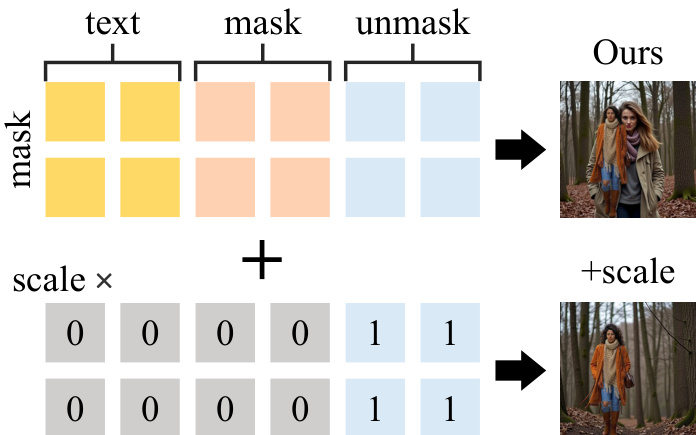
To further enhance the method's capabilities, the authors propose two optional techniques. The first is a reinitialization step, where the noise at the final inversion timestep is replaced with a fused noise vector to disrupt any residual information from the original object, which is particularly useful for object removal tasks. The second technique involves using an attention mask during the inversion process to prevent the foreground content from being incorporated into the key-value pairs, thereby reducing the propagation of original content information. These enhancements are designed to improve the method's performance in diverse editing scenarios.
Experiment
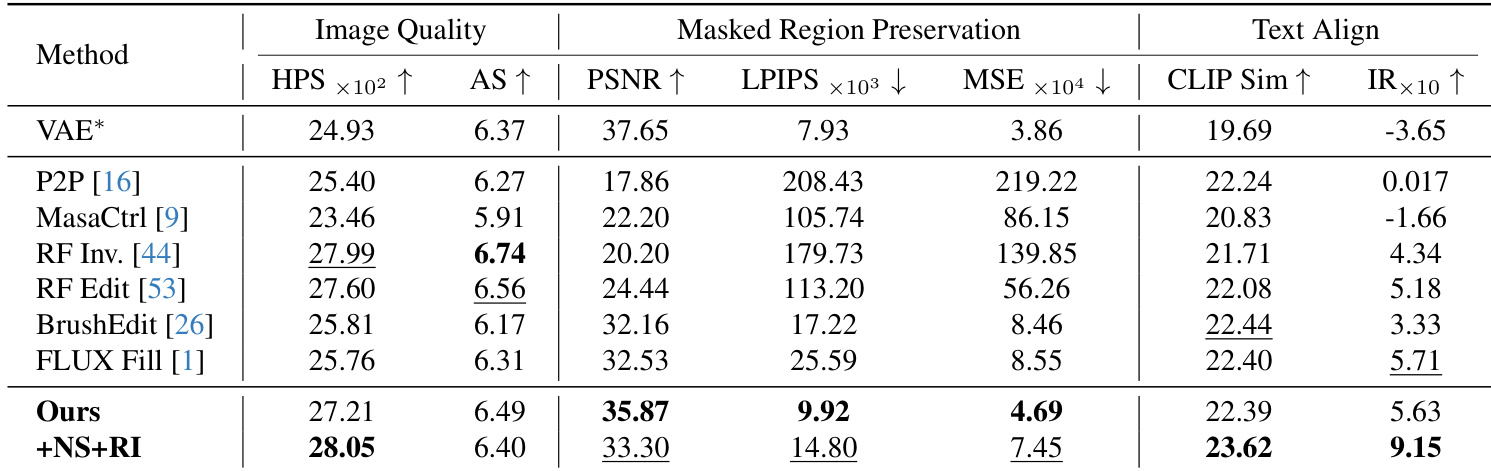
- Evaluated against six baselines on PIE-Bench, including training-free (P2P, MasaCtrl, RF-Edit, RF-Inversion) and training-based methods (BrushEdit, FLUX-Fill), using nine tasks from 620 images.
- Achieved the best performance in background preservation (PSNR, LPIPS, MSE), with PSNR values consistently above 30, ensuring consistent background fidelity.
- Surpassed all baselines in text-image alignment, achieving the highest CLIP score and Image Reward, particularly with reinitialization strategy.
- On PIE-Bench, our method achieved third-best image quality (HPSv2, aesthetic score) while outperforming training-based methods in background preservation and overall satisfaction.
- User study with 20+ participants showed our method significantly outperforms baselines across image quality, background preservation, text alignment, and overall satisfaction, even surpassing FLUX-Fill.
- Ablation studies confirmed that reinitialization and no-skip steps improve text alignment, though they slightly reduce image quality in cases with large masks; attention masking enhances performance in specific scenarios.
- Demonstrated flexibility in object removal, color change, and inpainting tasks, with reinitialization enabling effective editing even in inpainting scenarios.
- Proposed attention scale mechanism to mitigate generation bias from large masks, improving content coherence in background editing.
- Inversion-based KV-Edit enables multiple edits after a single inversion, offering superior workflow efficiency and lower artifact risk compared to inversion-free alternatives.
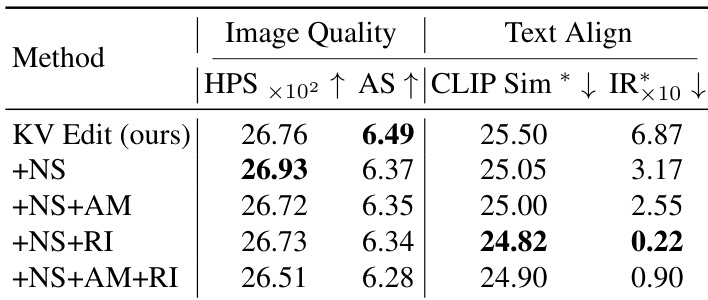
Results show that the proposed KV Edit method achieves the best image quality and text alignment scores among all variants. The addition of reinitialization (RI) significantly improves text alignment, with the +NS+RI variant achieving the highest CLIP Sim and lowest IR scores, indicating strong prompt adherence, while the +NS+AM+RI combination further enhances performance, though with a slight trade-off in image quality.
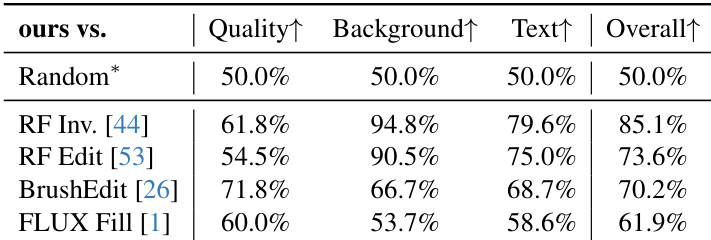
The authors compare their method against four baselines in a user study, evaluating image quality, background preservation, text alignment, and overall satisfaction. Results show that their method significantly outperforms all baselines across all criteria, achieving the highest win rates in every category.
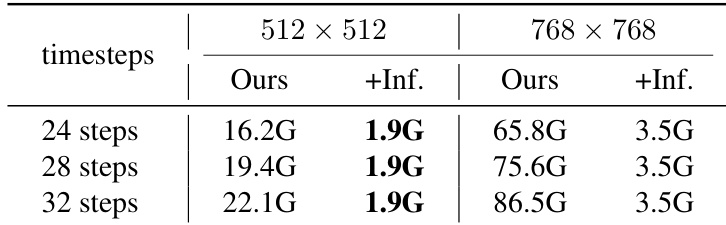
Results show that the memory usage of the inversion-based method increases with the number of timesteps and image resolution, while the inversion-free method maintains a constant memory footprint. The inversion-free approach reduces memory consumption significantly, using only 1.9G for 24 steps at 512×512 and 3.5G at 768×768, compared to 16.2G and 65.8G for the inversion-based method under the same conditions.
The authors use a comprehensive evaluation on PIE-Bench to compare their method against six baselines across image quality, background preservation, and text alignment. Results show that their approach achieves the best performance in masked region preservation and text alignment, outperforming both training-free and training-based methods, while maintaining high image quality.