Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
OmniConsistency: Learning Style-Agnostic Consistency from Paired
Stylization Data
OmniConsistency: Learning Style-Agnostic Consistency from Paired Stylization Data
Song Yiren Liu Cheng Shou Mike Zheng
Abstract
Diffusion models have advanced image stylization significantly, yet two core challenges persist: (1) maintaining consistent stylization in complex scenes, particularly identity, composition, and fine details, and (2) preventing style degradation in image-to-image pipelines with style LoRAs. GPT-4o's exceptional stylization consistency highlights the performance gap between open-source methods and proprietary models. To bridge this gap, we propose extbf{OmniConsistency}, a universal consistency plugin leveraging large-scale Diffusion Transformers (DiTs). OmniConsistency contributes: (1) an in-context consistency learning framework trained on aligned image pairs for robust generalization; (2) a two-stage progressive learning strategy decoupling style learning from consistency preservation to mitigate style degradation; and (3) a fully plug-and-play design compatible with arbitrary style LoRAs under the Flux framework. Extensive experiments show that OmniConsistency significantly enhances visual coherence and aesthetic quality, achieving performance comparable to commercial state-of-the-art model GPT-4o.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Show Lab, National University of Singapore propose OmniConsistency, a plug-and-play diffusion transformer-based framework that enables style-consistent image stylization across diverse scenes and unseen style LoRAs by combining in-context consistency learning and a two-stage progressive training strategy, significantly reducing style degradation and matching GPT-4o-level performance.
Key Contributions
- OmniConsistency addresses the persistent challenges of style inconsistency and degradation in complex image-to-image stylization by introducing an in-context consistency learning framework trained on aligned image pairs, enabling robust generalization across diverse styles without requiring style-specific retraining.
- The method employs a two-stage progressive learning strategy that decouples style learning from consistency preservation, combined with a lightweight Consistency LoRA Module and Conditional Token Mapping, effectively mitigating style degradation while maintaining high computational efficiency.
- Extensive evaluations on a newly curated dataset of 22 diverse styles demonstrate that OmniConsistency achieves state-of-the-art performance in both style and content consistency, matching the high-quality output of commercial models like GPT-4o across various benchmarks.
Introduction
Diffusion models have become the dominant force in image stylization, particularly with transformer-based architectures like DiT offering superior fidelity and prompt alignment. However, existing methods struggle with maintaining consistent stylization across complex scenes—especially in preserving identity, composition, and fine details—when applied to image-to-image pipelines using style LoRAs. A key limitation is style degradation caused by structural constraints from modules like ControlNet, which undermines stylization quality and coherence. The authors introduce OmniConsistency, a plug-and-play consistency module built on Diffusion Transformers that decouples style learning from consistency preservation via a two-stage progressive training strategy. It leverages in-context learning from paired stylization data and introduces a rolling LoRA Bank loader, a lightweight Consistency LoRA Module, and a Conditional Token Mapping scheme to enhance generalization and efficiency. The method achieves style-agnostic consistency across diverse and unseen styles, matching the performance of proprietary models like GPT-4o, and is released with a new benchmark dataset and evaluation protocol based on GPT-4o for standardized assessment.
Dataset
- The dataset is constructed entirely through GPT-4o-driven generation, using publicly sourced and legally compliant input images that are carefully curated.
- For each of 22 distinct artistic styles—such as anime, sketch, chibi, pixel-art, watercolor, oil painting, and cyberpunk—GPT-4o generates stylized image versions alongside descriptive text annotations for both the original and stylized images.
- A human-in-the-loop filtering pipeline reviews over 5,000 candidate image pairs to remove instances with issues like gender mismatches, incorrect age or skin tone, detail distortions, pose discrepancies, inconsistent styles, or layout misalignments.
- After filtering, 80 to 150 high-quality image pairs are retained per style, resulting in a final dataset of 2,600 verified image pairs.
- Input images for each style are kept mutually exclusive to ensure diversity, including complex scenes such as multi-person portraits.
- The dataset is used to train the model with a mixture of styles, where each style contributes proportionally to the training mix based on its representation in the curated set.
- No image cropping is applied; instead, the original image dimensions are preserved to maintain structural fidelity.
- Metadata is constructed during generation, including style labels, source image identifiers, and annotation consistency checks, which are used to guide training and evaluation.
Method
The authors leverage a two-stage training pipeline and a set of modular components to achieve robust style-agnostic consistency in image stylization. The overall framework, illustrated in the figure below, consists of a style learning phase followed by a consistency learning phase, designed to decouple stylistic adaptation from structural preservation. In the first stage, individual LoRA modules are trained on dedicated datasets to capture unique stylistic characteristics, forming a style LoRA bank. The second stage trains a consistency LoRA module on the same paired data, dynamically switching between the pre-trained style LoRA modules during training to optimize for content integrity across diverse stylizations. This decoupling strategy prevents interference between style and consistency objectives, enhancing generalization.
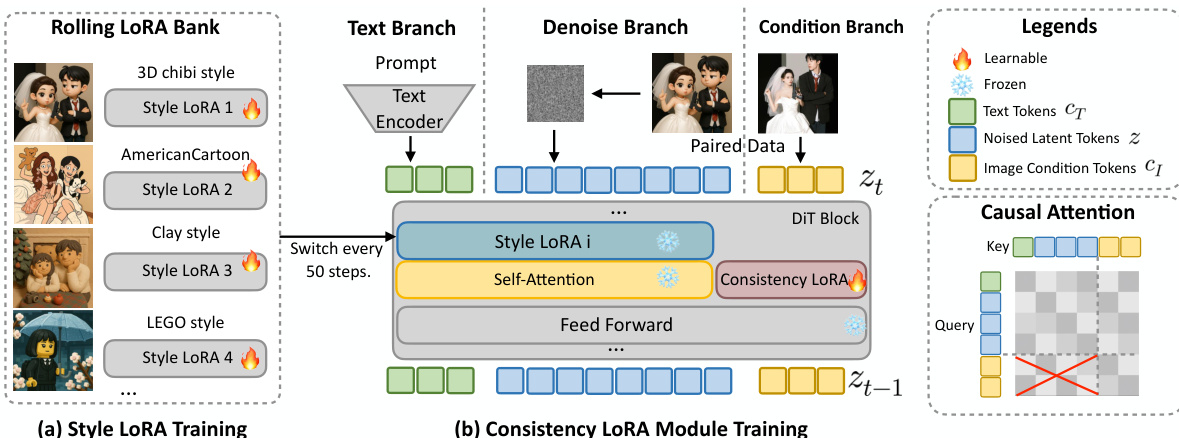
The framework introduces two key architectural components to improve disentanglement and efficiency. The first is the Consistency LoRA Module, which injects condition-specific information through a dedicated low-rank adaptation path applied exclusively to the condition branch of the diffusion transformer. This design isolates consistency learning from the stylization pathway, ensuring compatibility and preventing parameter entanglement. Formally, given input features Zt, Zn, and Zc for the text, noise, and condition branches, the standard QKV projections are defined as Qi=WQZi, Ki=WKZi, and Vi=WVZi for i∈{t,n,c}. To inject conditional information, LoRA transformations are applied solely to the condition branch, resulting in ΔQc=BQAQZc, ΔKc=BKAKZc, and ΔVc=BVAVZc, where A and B are low-rank adaptation matrices. The updated QKV for the condition branch becomes Qc′=Qc+ΔQc, Kc′=Kc+ΔKc, and Vc′=Vc+ΔVc, while the text and noise branches remain unaltered. This ensures that consistency-related adaptation is introduced in an isolated manner without interfering with the backbone's stylization capacity.
The second architectural component is a position-aware interpolation and feature reuse mechanism. To improve computational efficiency, the framework employs Conditional Token Mapping (CTM) to guide high-resolution generation using a low-resolution condition image. Given original resolution (M,N) and condition resolution (H,W), scaling factors Sh=M/H and Sw=N/W are defined. Each token (i,j) in the downsampled condition maps to position (Pi,Pj) in the high-resolution grid, where Pi=i⋅Sh and Pj=j⋅Sw, preserving pixel-level correspondence. Additionally, Feature Reuse is implemented by caching the intermediate key-value projections of condition tokens during inference and reusing them across denoising steps, significantly reducing inference time and GPU memory usage without compromising generation quality. The framework also employs causal attention, where condition tokens can only attend to each other and are blocked from accessing noise/text tokens, while the main branch follows standard causal attention and can attend to condition tokens. This design maintains clean causal modeling and prevents conflicts between stylization and consistency.
Experiment
- Conducted two-stage training: fine-tuning style LoRA for 6,000 steps on a single GPU, followed by training the consistency module for 9,000 steps on 4 GPUs with rolling LoRA bank to enable multi-style generalization.
- Evaluated on a new 100-image benchmark with complex compositions and 5 unseen style LoRAs (comic, oil painting, PVC toys, sketch, vector), using DreamSim, CLIP Image Score, GPT-4o Score, FID, and CMMD.
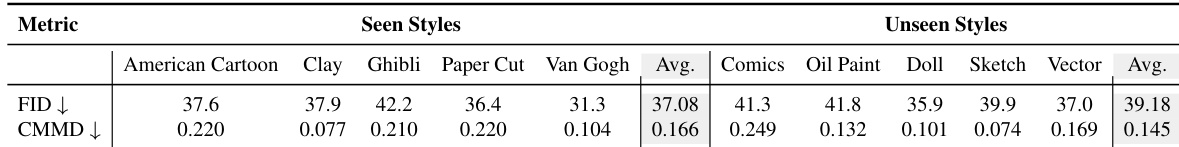
- Achieved state-of-the-art results on style consistency metrics and highest CLIP Score, demonstrating superior text-image alignment and balanced stylization fidelity, content preservation, and prompt alignment.
- Outperformed baselines including Flux I2I, Redux, ControlNet, and GPT-4o in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations, with results comparable to GPT-4o while maintaining better structural and style consistency.
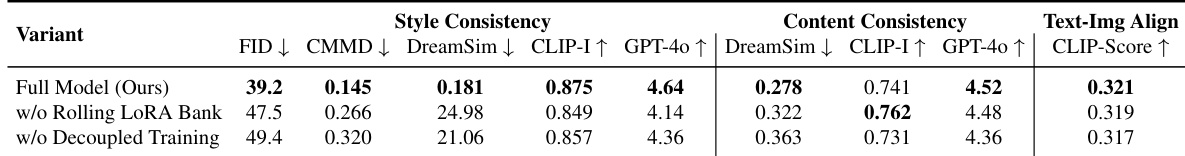
- Ablation studies confirmed that rolling training with multiple LoRAs and decoupled training of style and consistency are critical for performance, especially on unseen styles.
- Demonstrated strong generalization to unseen styles with minimal performance drop (FID/CMMD scores in Table 3), plug-and-play compatibility with IP-Adapter and text-guided pipelines, and low overhead (4.6% higher GPU memory, 5.3% longer inference time).
- User study (n=30) showed higher preference for both style and content consistency compared to baselines, with GPT-4o used as a reference despite prompt-based approximation due to LoRA incompatibility.
- Limitations include difficulty preserving non-English text and occasional artifacts in small facial/hand regions, particularly in complex scenes with multiple people.
The authors use a benchmark of 100 images with complex compositions to evaluate their method against several baselines, including Flux pipelines, ControlNet, and GPT-4o. Results show that their method achieves the best performance across five style consistency metrics and ranks among the top in content consistency, while also obtaining the highest CLIP Score, indicating superior text-image alignment.
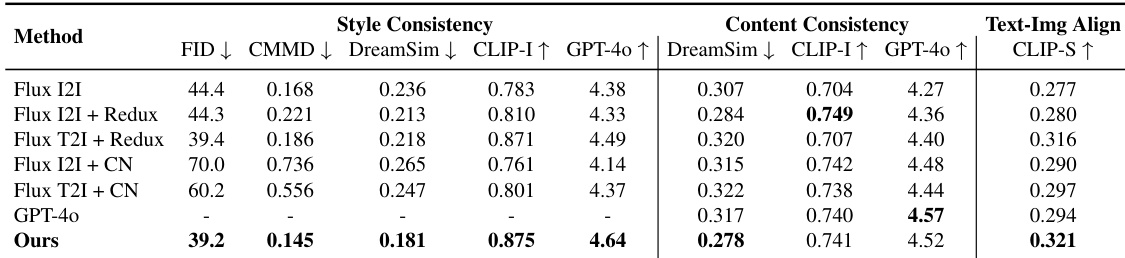
Results show that OmniConsistency achieves strong style consistency across both seen and unseen styles, with FID and CMMD scores indicating minimal degradation on unseen styles compared to seen ones. The method maintains high performance in style and content consistency, demonstrating effective generalization to diverse and previously unseen LoRA styles.
The authors use a two-stage training process to develop OmniConsistency, combining a style LoRA fine-tuning stage with a consistency module training stage that leverages a rolling LoRA bank to promote multi-style generalization. Results show that the full model achieves the best performance across all metrics, particularly in style consistency and text-image alignment, while ablation studies confirm that both the rolling LoRA bank and decoupled training are essential for maintaining high-quality stylization and content preservation.